[ad_1]
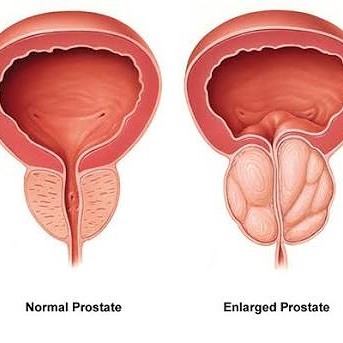
DEFINITION
Prostate gland enlargement is a common condition as men get older. Also called benign prostatic hyperplasia (BPH), prostate gland enlargement can cause bothersome urinary symptoms. Untreated, prostate gland enlargement can block the flow of urine out of the bladder and cause bladder, urinary tract or kidney problems.
There are several effective treatments for prostate gland enlargement, including medications, minimally invasive therapies and surgery. To choose the best option, you and your doctor will consider your symptoms, the size of your prostate, other health conditions you might have and your preferences.
SYMPTOMS
The severity of symptoms in people who have prostate gland enlargement varies, but symptoms tend to gradually worsen over time. Common signs and symptoms of BPH include:
Frequent or urgent need to urinate
Increased frequency of urination at night (nocturia)
Difficulty starting urination
Weak urine stream or a stream that stops and starts
Dribbling at the end of urination
Straining while urinating
Inability to completely empty the bladder
Less common signs and symptoms include:
Urinary tract infection
Inability to urinate
Blood in the urine
The size of your prostate doesn’t necessarily mean your symptoms will be worse. Some men with only slightly enlarged prostates can have significant symptoms, while other men with very enlarged prostates can have only minor urinary symptoms.
In some men, symptoms eventually stabilize and might even improve over time.
Other possible causes of urinary symptoms
Conditions that can lead to symptoms similar to those caused by enlarged prostate include:
Urinary tract infection
Inflammation of the prostate (prostatitis)
Narrowing of the urethra (urethral stricture)
Scarring in the bladder neck as a result of previous surgery
Bladder or kidney stones
Problems with nerves that control the bladder
#Lagos #Naija #Medicinalplants #nat #Sunnah #planetfit
[ad_2]
Source
